2.OS Structures
约 343 个字 预计阅读时间 1 分钟
Sorts of OS¶
-
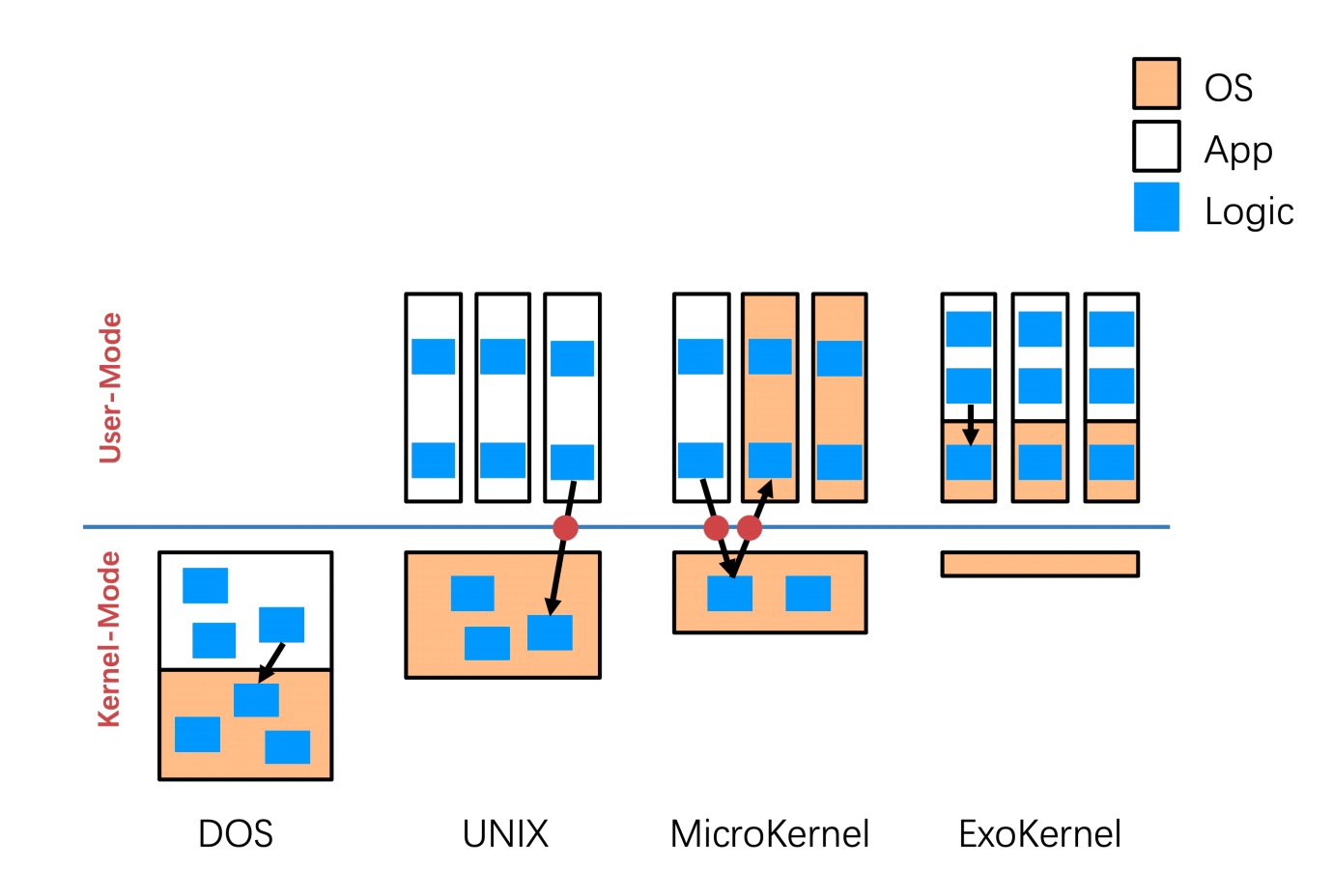
Simple Structure: MS-DOS
- 对各个部分不做隔离;
-
Monolithic Structure – Original UNIX
- 优点:性能比较好,不需要频繁的切换态;
- 缺点:
- 安全性较弱,把很大一部分放在内核里,如果一点有问题,那就全部完蛋了,所以我们希望执行在内核态的代码越少越好,比如设备驱动程序;
- 可扩展性较差,可以加载LKM(可加载内存模块)文件,但是这些文件与操作系统版本紧密绑定;
-
Microkernel System Structure(微内核)
- 优点:
- 用于解决整体性结构的安全性问题;
- 扩展性好;
- 可调试性;
- 缺点:
- 开销很大,多态之间的切换和数据的拷贝;
- 优点:
-
Exokernel: Motivation
- 更少的抽象
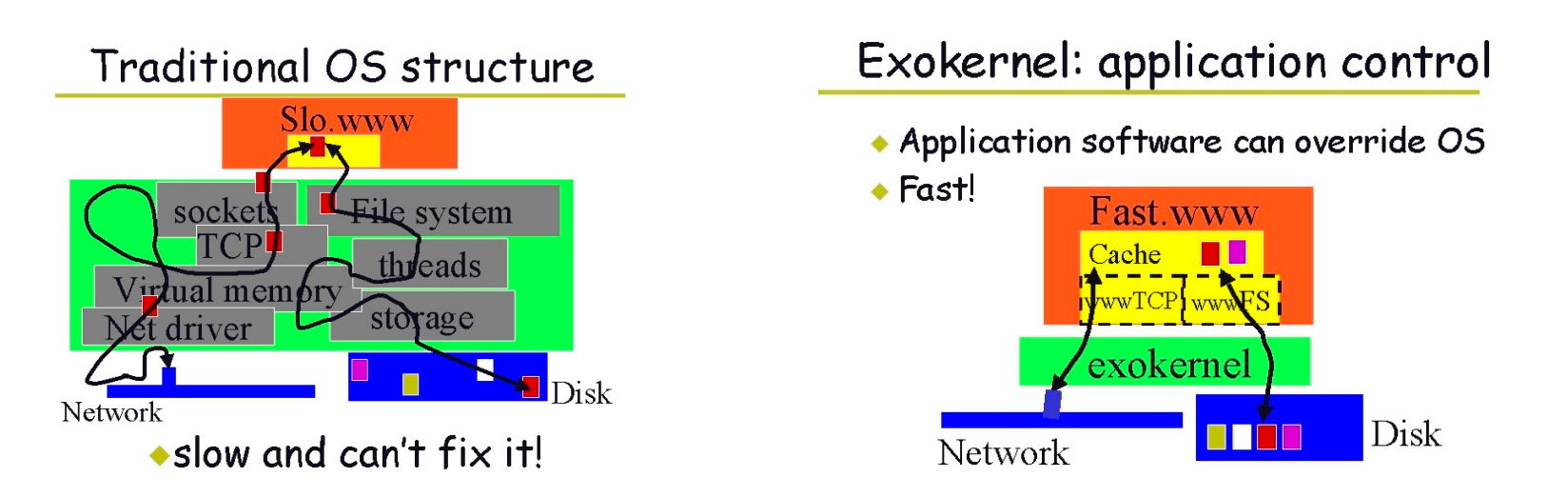
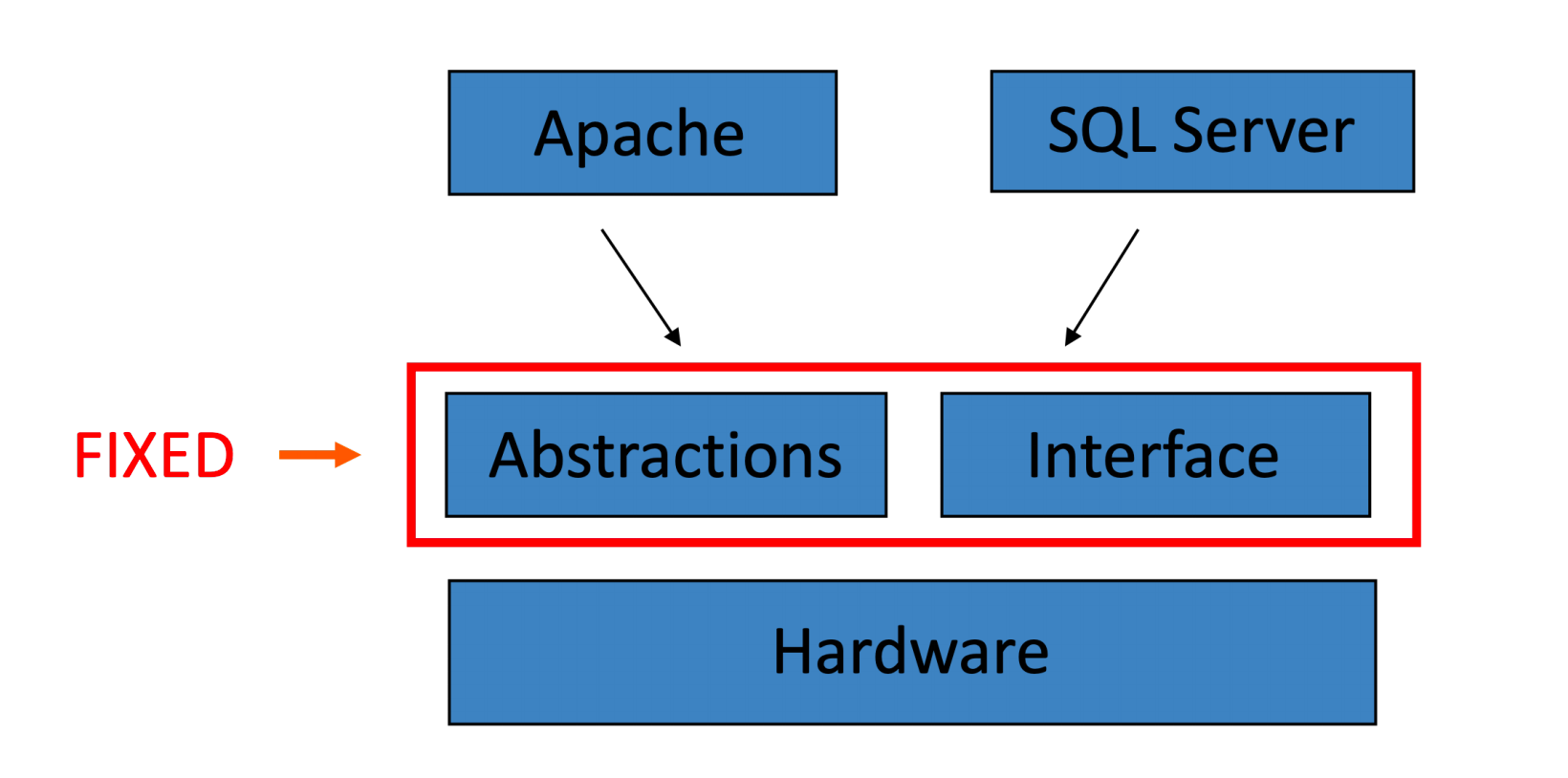
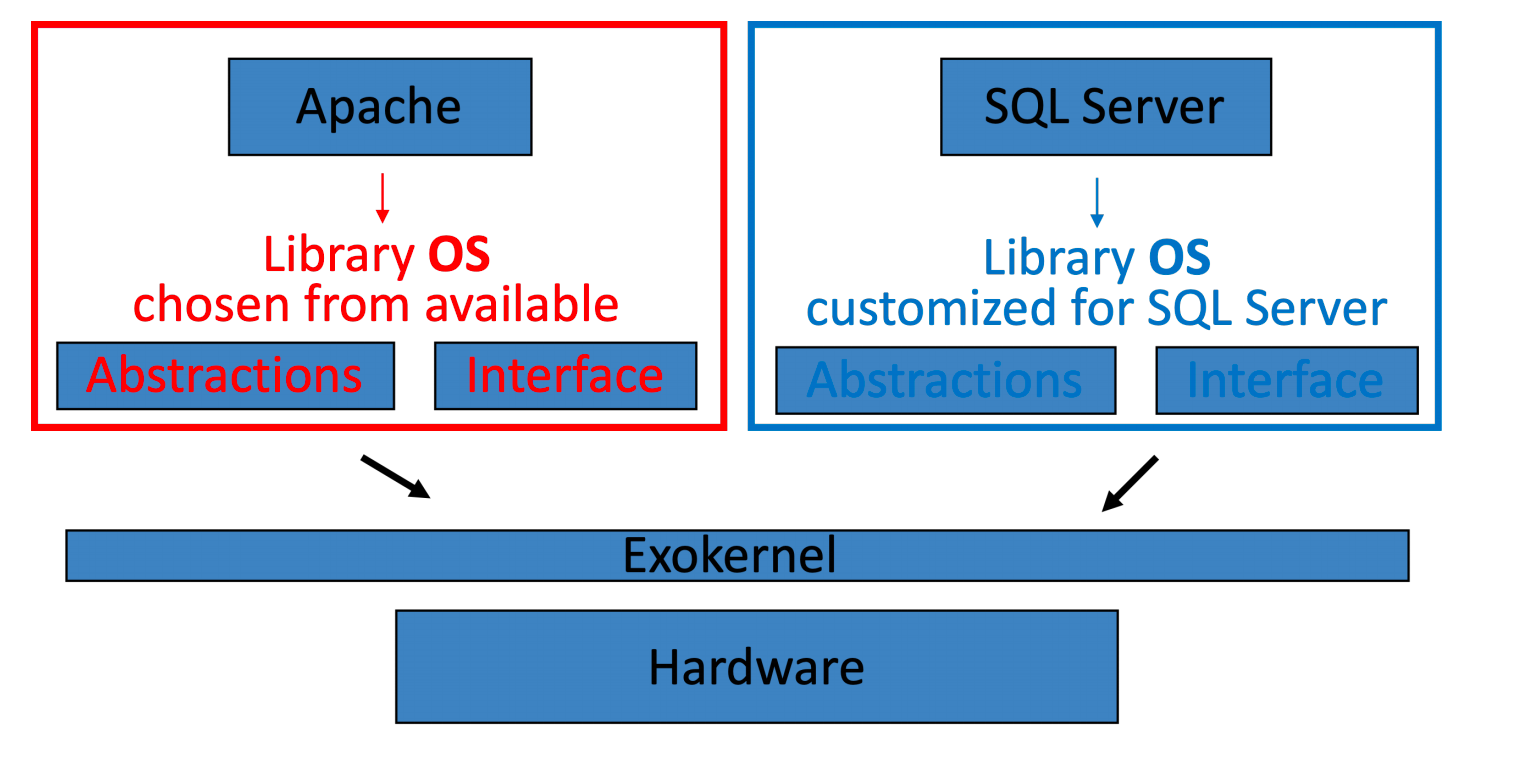
Comparison¶
Tracing¶
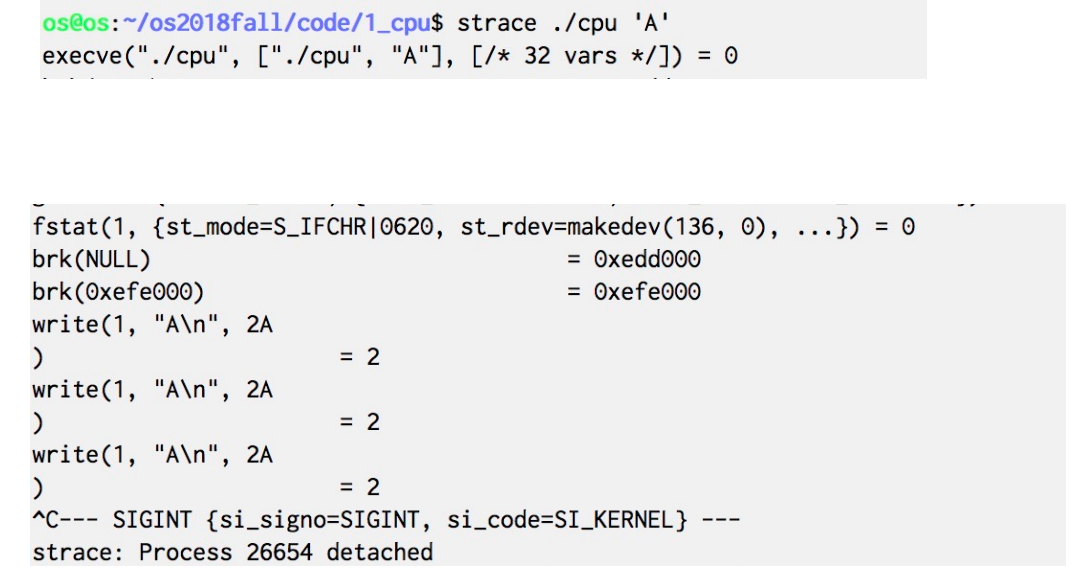
- strace – trace system calls invoked by a process(列出进程中所有的系统调用)
- gdb – source-level debugger
- perf – collection of Linux performance tools
- tcpdump – collects network packets
总结¶
- 系统调用(程序和操作系统的调用)
- 系统调用参数传递
- 系统调用的实现
- 各种操作系统结构
System Call Examples¶
1. fork()¶
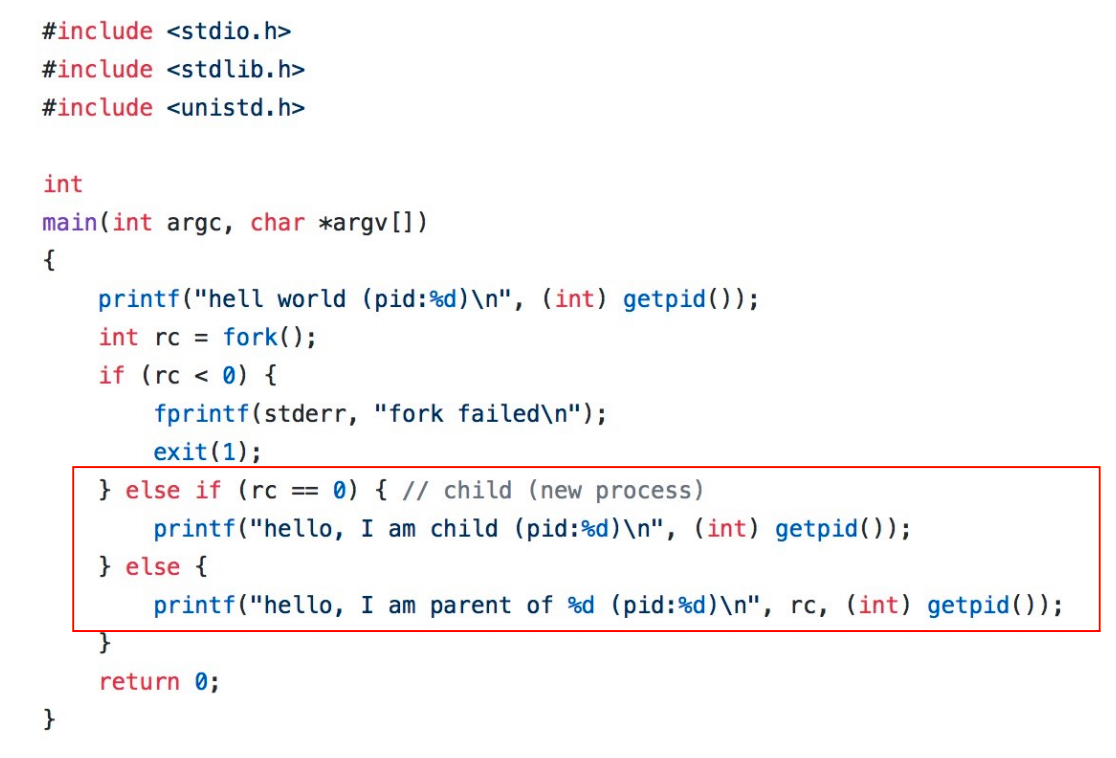
2. fork + wait¶
Parent process can use the wait system call to wait the child process finishes executing.

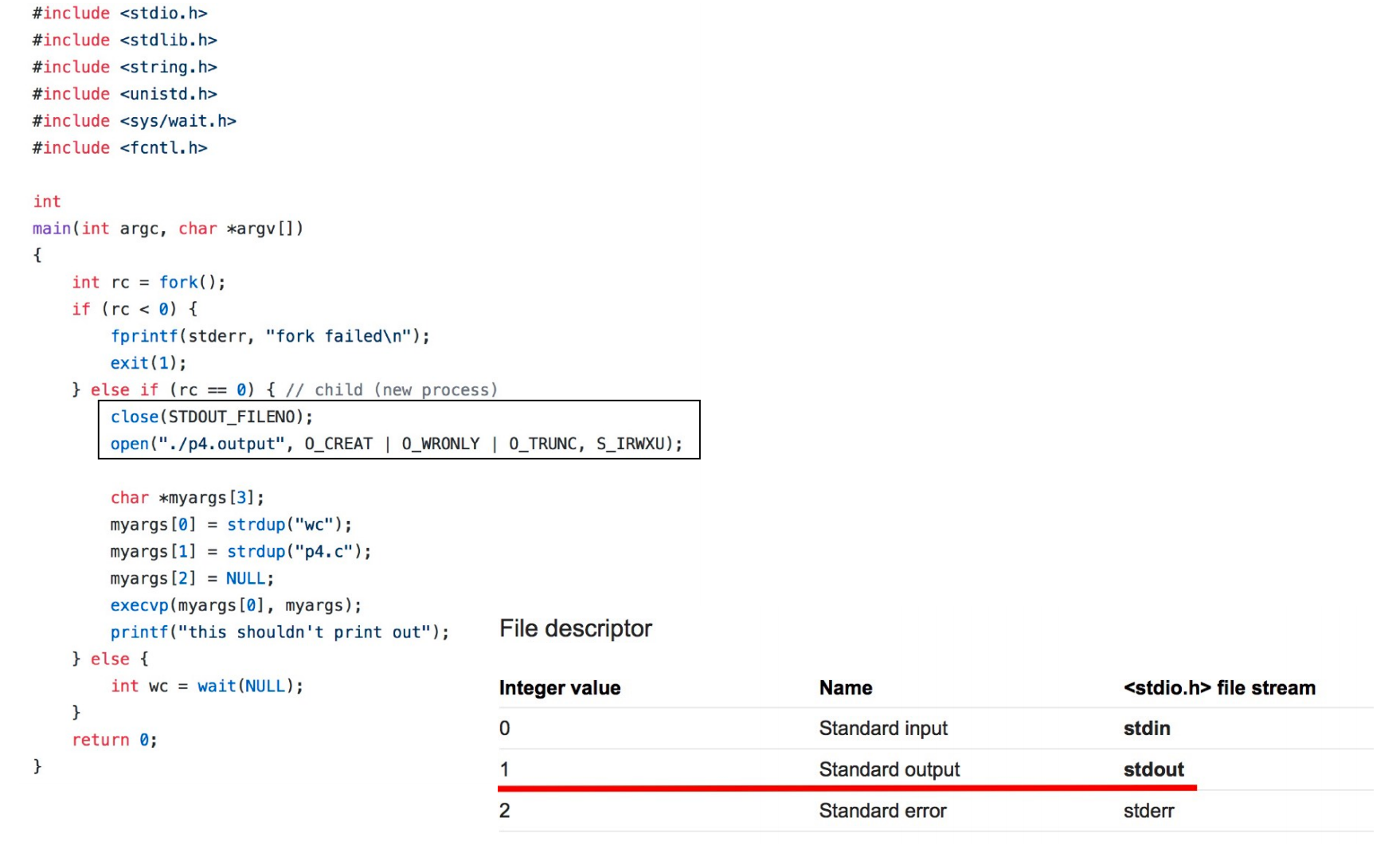
3. fork + wait + exec¶
wc是一个program,这样,子进程就加载了另外一个program;

可以在exec前做一些精巧的控制;
4. ptrace¶
没怎么听。。。
5. set breakpoint¶
执行CPU异常,让父进程得到运行,以此来控制;
本文总阅读量次