5.Threads_b
约 103 个字 126 行代码 7 张图片 预计阅读时间 2 分钟
Light-Weight Processes: Dissecting Linux Threads¶
1. Thread¶
2. How does Linux implement threads?¶
-

-
NLWP就是一个进程中的线程数;
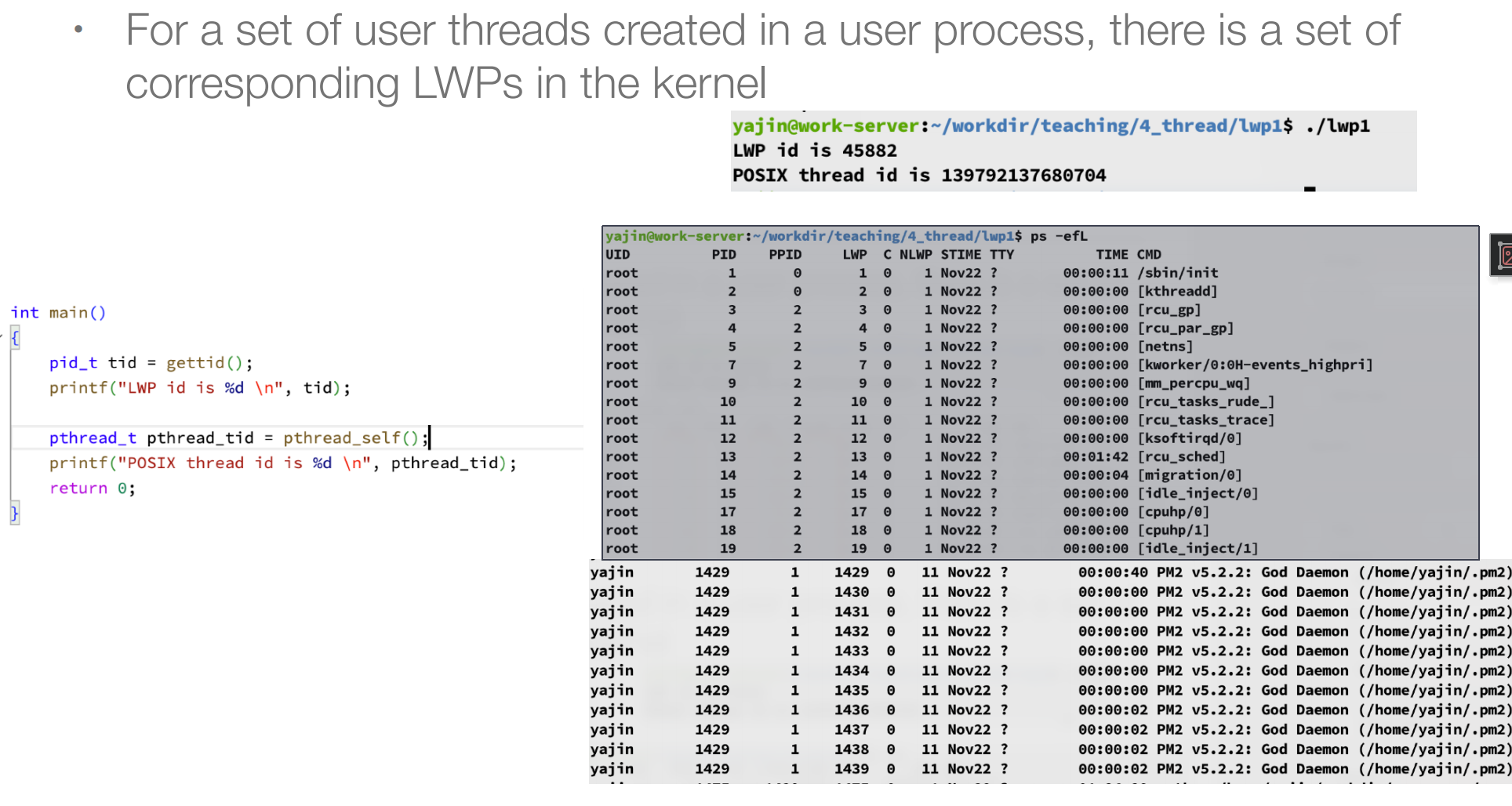
3. What is a Light-Weight Process¶
- LWP就是linux概念下的内核线程;

4. How to create LWP¶
-
fork完全可以通过clone来实现,clone通过flag来控制资源是否共享;
-

5. 具体例子¶
C
#define _GNU_SOURCE /* See feature_test_macros(7) */
#include <sched.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sched.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 64kB stack
#define STACK 1024*64
// The child thread will execute this function
int threadFunction( void* argument ) {
printf( "child thread entering\n" );
close((uintptr_t)argument);
printf( "child thread exiting\n" );
return 0;
}
int main() {
void* stack;
pid_t pid;
int fd;
fd = open("/dev/null", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("/dev/null");
exit(1);
}
// Allocate the stack
stack = malloc(STACK);
if (stack == 0) {
perror("malloc: could not allocate stack");
exit(1);
}
printf("Creating child thread\n");
// Call the clone system call to create the child thread
pid = clone(&threadFunction, //
(char*) stack + STACK, //子进程栈在哪里
SIGCHLD | CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES |
CLONE_SIGHAND | CLONE_VM,
(void *)(uintptr_t)fd);
if (pid == -1) {
perror("clone");
exit(2);
}
// Wait for the child thread to exit
pid = waitpid(pid, 0, 0);
if (pid == -1) {
perror("waitpid");
exit(3);
}
// Attempt to write to file should fail, since our thread has
// closed the file.
if (write(fd, "c", 1) < 0) {
printf("Parent:\t child closed our file descriptor\n");
}
// Free the stack
free(stack);
return 0;
}
C
- CLONE_VM:共享memory;
- #define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <sched.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
static int child_func(void* arg) {
char* buf = (char*)arg;
printf("[Child] Child sees buf = %p - \"%s\"\n", buf, buf);
strcpy(buf, "hello from child");
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
// Allocate stack for child task.
const int STACK_SIZE = 65536;
char* stack = malloc(STACK_SIZE);
if (!stack) {
perror("malloc");
exit(1);
}
// When called with the command-line argument "vm", set the CLONE_VM flag on.
unsigned long flags = 0;
if (argc > 1 && !strcmp(argv[1], "vm")) {
flags |= CLONE_VM;
}
char buf[100];
strcpy(buf, "hello from parent");
if (clone(child_func, stack + STACK_SIZE, flags | SIGCHLD, buf) == -1) {
perror("clone");
exit(1);
}
int status;
if (wait(&status) == -1) {
perror("wait");
exit(1);
}
printf("[Parent] Child exited with status %d. buf = %p - \"%s\"\n", status,buf, buf);
return 0;
}

- 在fork情况下,父进程和子进程共享file descriptor(文件描述符 ),但不共享memory;
本文总阅读量次

