2.Basic Principles
约 531 个字 6 张图片 预计阅读时间 2 分钟
第一课 4.24
一些基本概念¶
What is security?
- Confidentiality(私密性):An attacker cannot recover protected data;
- Integrity(完整性):An attacker cannot modify protected data;
- Availability(可用性):An attacker cannot stop/hinder computation(阻止别人访问到自己的服务);
Adversary(对手)
- 对手是任何试图绕过安全基础设施的个体;
Trust
-
信任是指一个实体的行为程度;
-
信任模型描述了对于某个特定环境,信任谁做什么;
Trusted Computing Base (TCB)

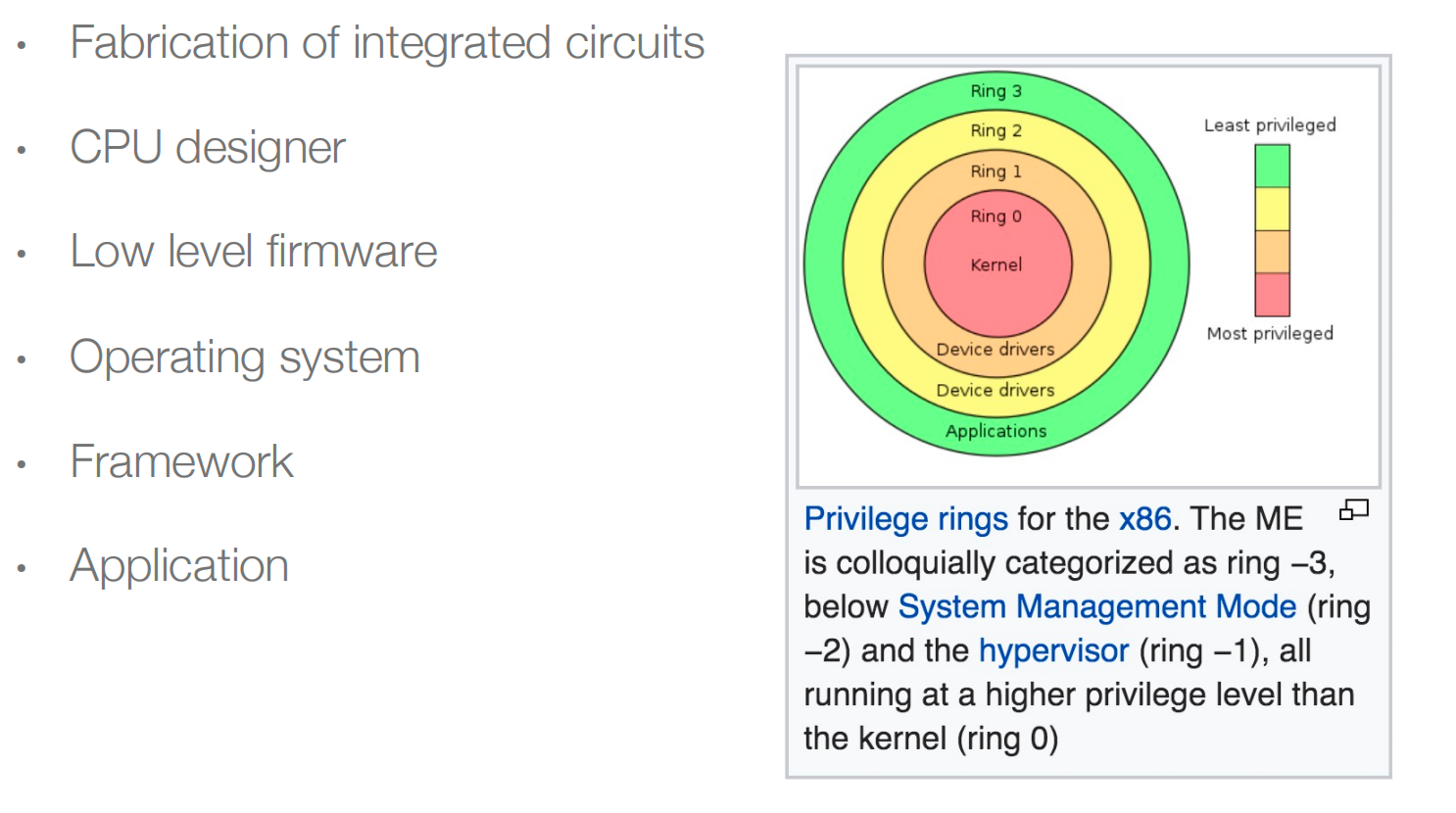
Threats

Policy and Enforcement
- Policy:谁被允许谁不允许做某事;
- Enforcement:强制使用policy的方法;
Fundamental Security Mechanism¶
- 隔离(Isolation)
One component cannot access data/code of the other component except through a well-defined API. For example, process.
- 最小特权(Least privilege)
最小特权原则确保组件具有运行所需的最小特权,从组件中进一步删除的任何特权都会删除某些功能。
- 错误隔离(Fault compartments)
和Isolation有粒度上的区别,错误隔离的粒度更细,指的是在一个component内存(比如在进程内部),对逻辑上不相关的部分进行隔离。
这样肯定是有代价的,隔离提高了安全性,同时降低了共享性,也就是效率会被降低。
- 信任和正确性(Trust and correctness)
根据规范,假设特定的组件是可信的或正确的。
正式验证确保组件正确地实现给定的规范,因此可以被信任。请注意,此属性是通常无法实现的理想属性。
问题:如何确保本规范的正确性?如果规范被更新了怎么办?
AAA¶
- Authentication: Who are you (what you know, have, or are)? 你是谁。
- Authorization: Who has access to object? 谁可以访问对象,验证完你是谁之后,你能干什么?
- Audit/Provenance: I’ll check what you did.
Authentication¶
- 你知道什么:用户名/密码(可以更换)
- 你是什么:一些生物特征(不能更换)
- 你有什么:second factor/智能卡
Authorization¶
这个人能够访问什么资源


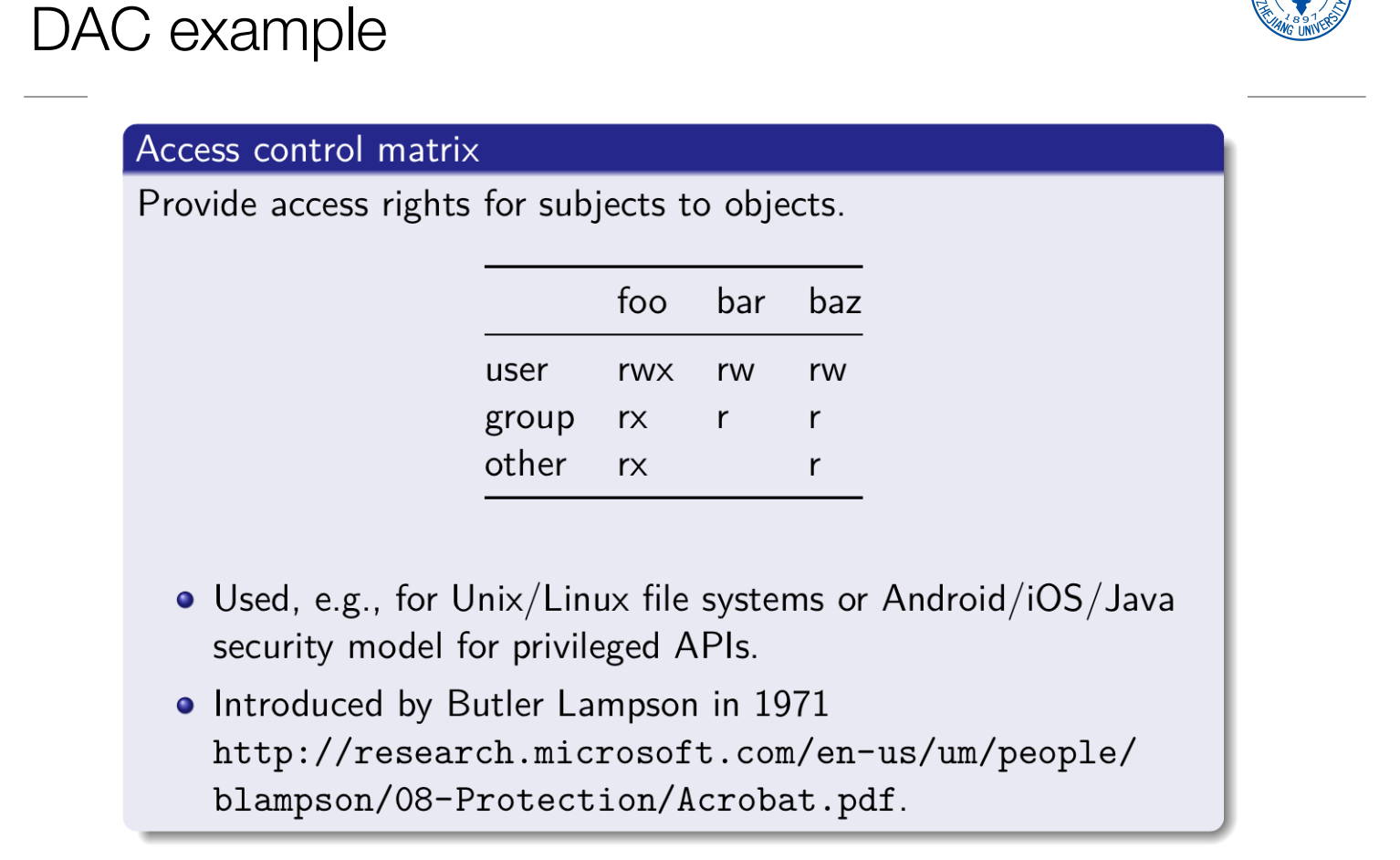
Vulnerabilities:vulnerability是指有能力利用该flaw的对手可以访问(威胁)的flaw。
Attacks:当有人想利用某个Vulnerabilities,那么攻击就产生了。
本文总阅读量次