lec7
约 409 个字 12 张图片 预计阅读时间 1 分钟
The disjoint set ADT¶
等价类划分,不是数据结构,是一个问题。
1. Equivalence Relations(等价关系)¶
特点:自反,对称,传递¶
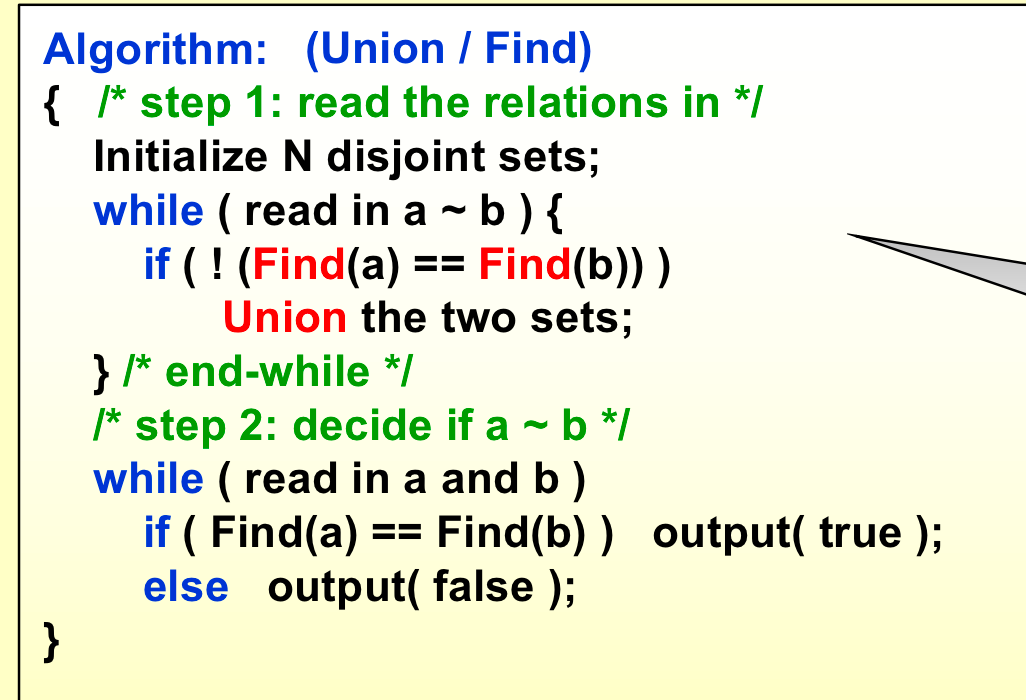
2. The Dynamic Equivalence Problem¶
2. 1 operations(管理集合)¶
Union:合并集合;find:查找元素所在集合;
2.2 实现¶
- 链表。
union方便,使用循环链表,但是find很麻烦。 - 树。把树合并,找到树的根两个操作。
3. Basic Data Structure¶
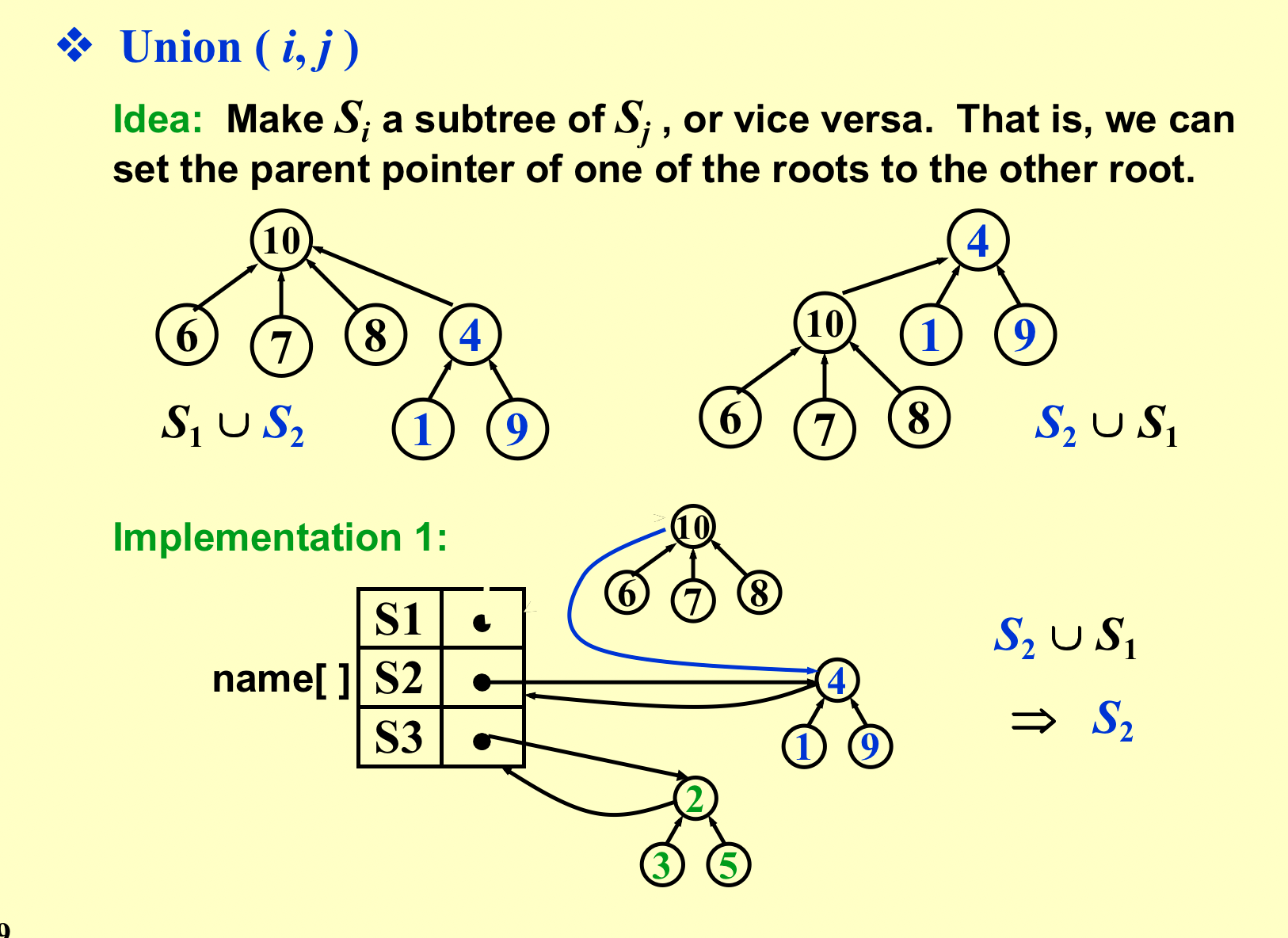
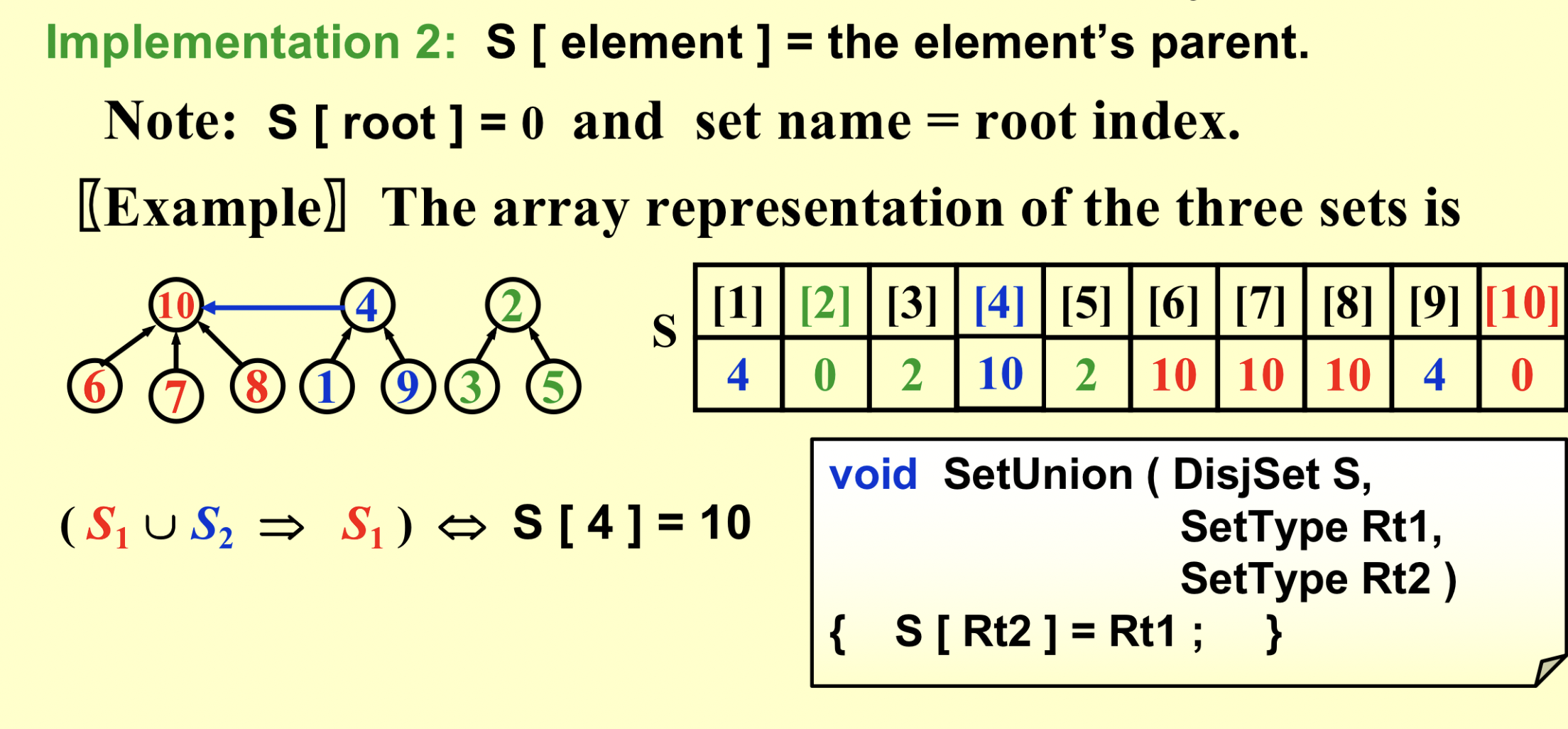
数组下标代表元素,数组数值代表parent指针。
union:把一个根赋值另一个根;
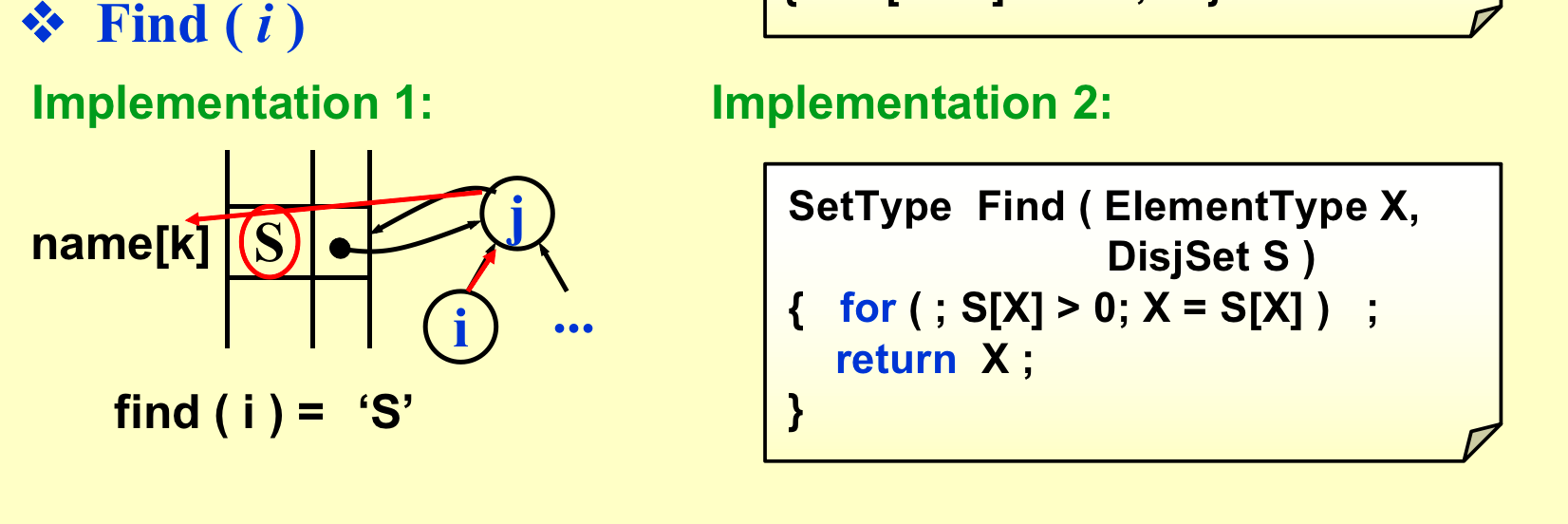
find:向上寻找;
4. Smart Union Algorithms(优化union操作)¶
- Union-by-Size

- Union-by-Height
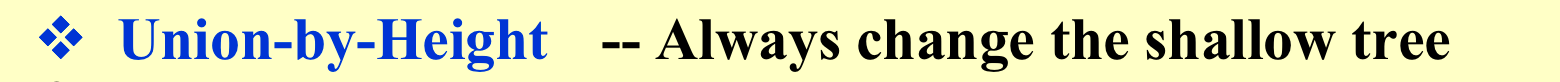
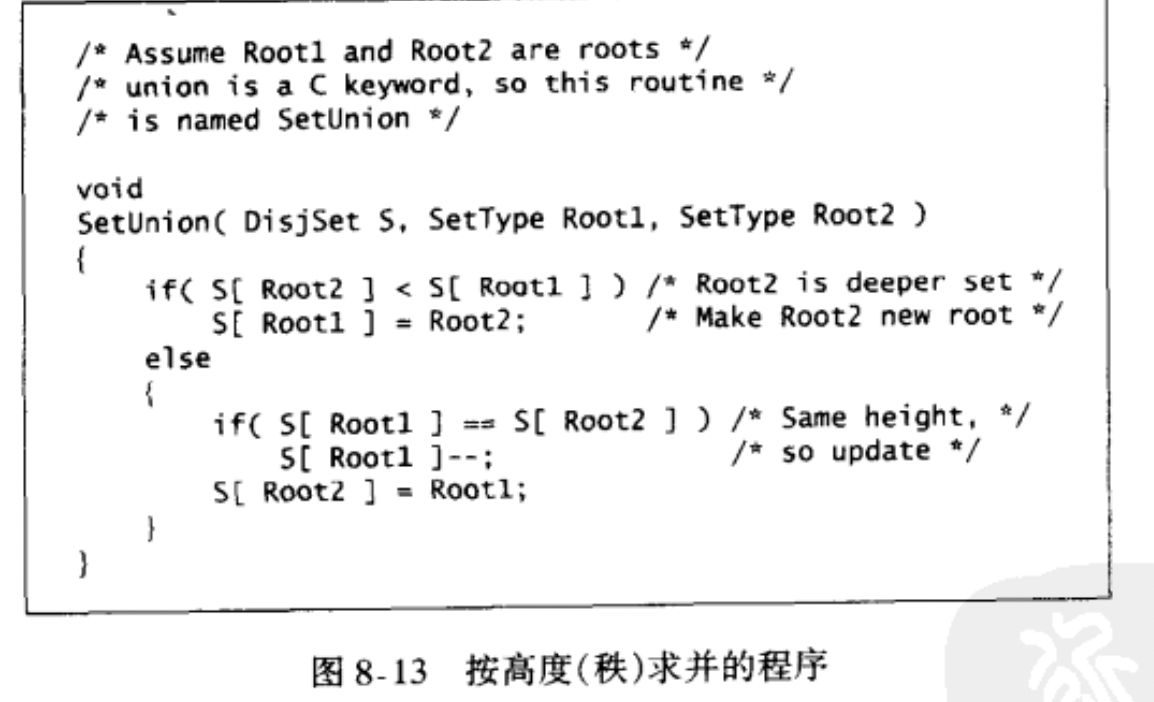
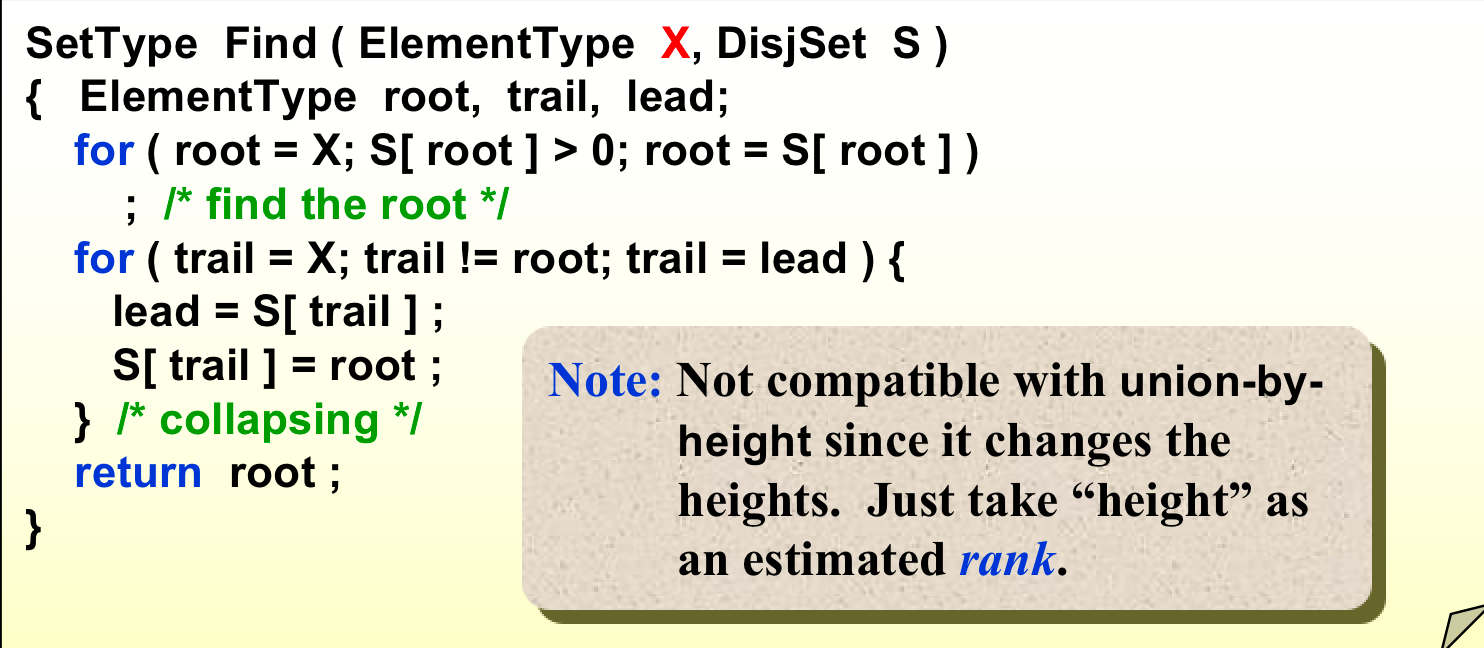
5. Path Compression(优化find操作)¶
find时,自动把路径上指向根。
两种实现算法¶
- 递归;

- 循环:两个指针一前一后;
6. Worst Case for Union-by-Rank and Path Compression¶
树是保证连通关系的最少边; Union-by-Height不能和Path Compression一起用;
期中考试¶
程序填空,判断题,选择题,期中考试到此为止;
Graph Algorithms¶
1. Definitions¶
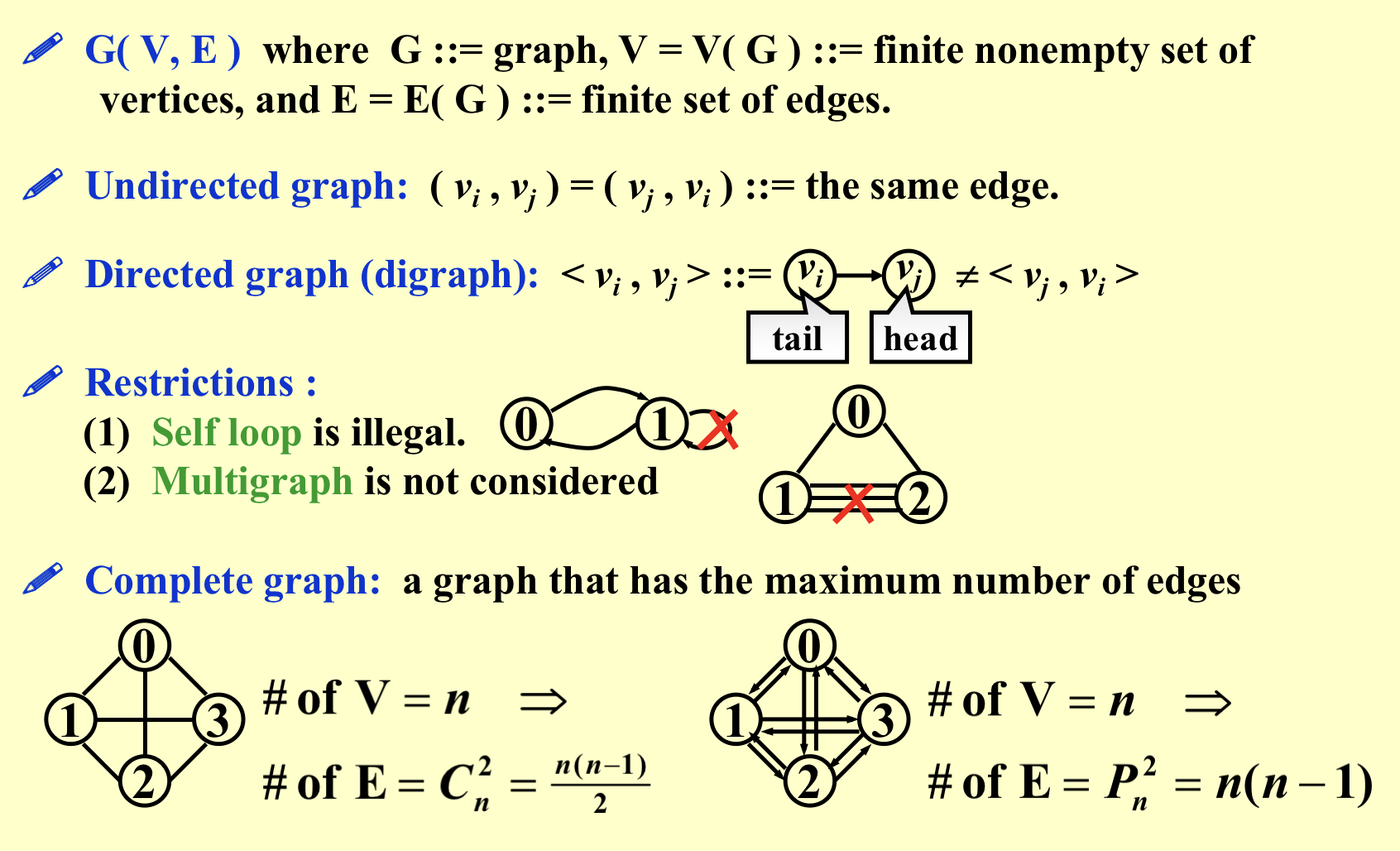
- G(V, E)
- Undirected graph(无向图)
- Directed graph(digraph)
- Compelet graph(完全图):任意两点都有线;
- adjacent:任意两点之间有边;
- subgraph:V,E都是子集;
- path(路径):一堆点的序列;
- simple path:路过的点不重复(头尾除外);
- Cycle:头尾一样;
- 两点间connect:之间有路径;
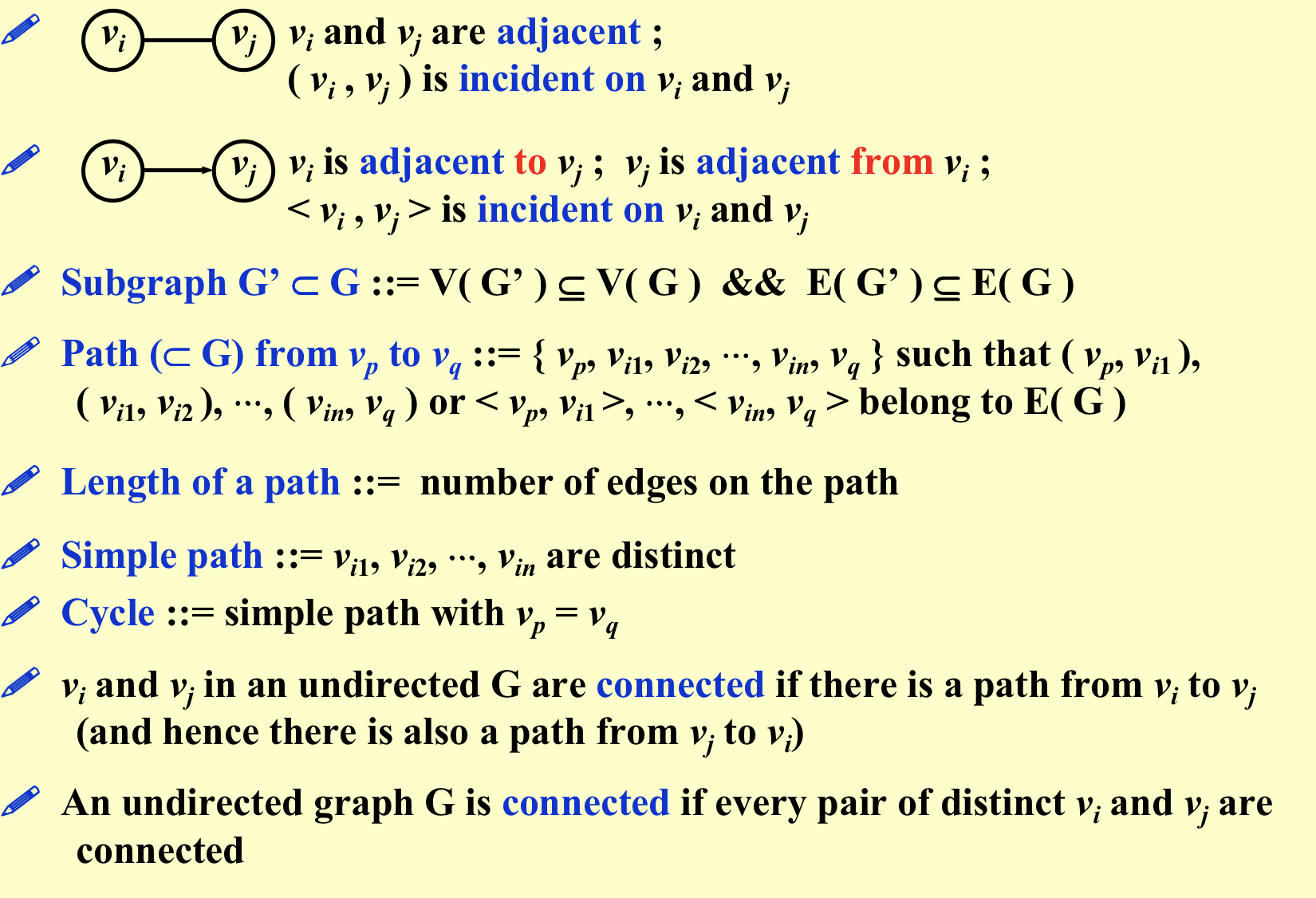
- 连通图:任意两点都是连通的;
- DAG:有向无环图;
- 强连通图:任何两点间都有路;
- 弱连通图:当成无向图是连通的;
- 强连通子图:
- degree(v):几条线,出度,入度;
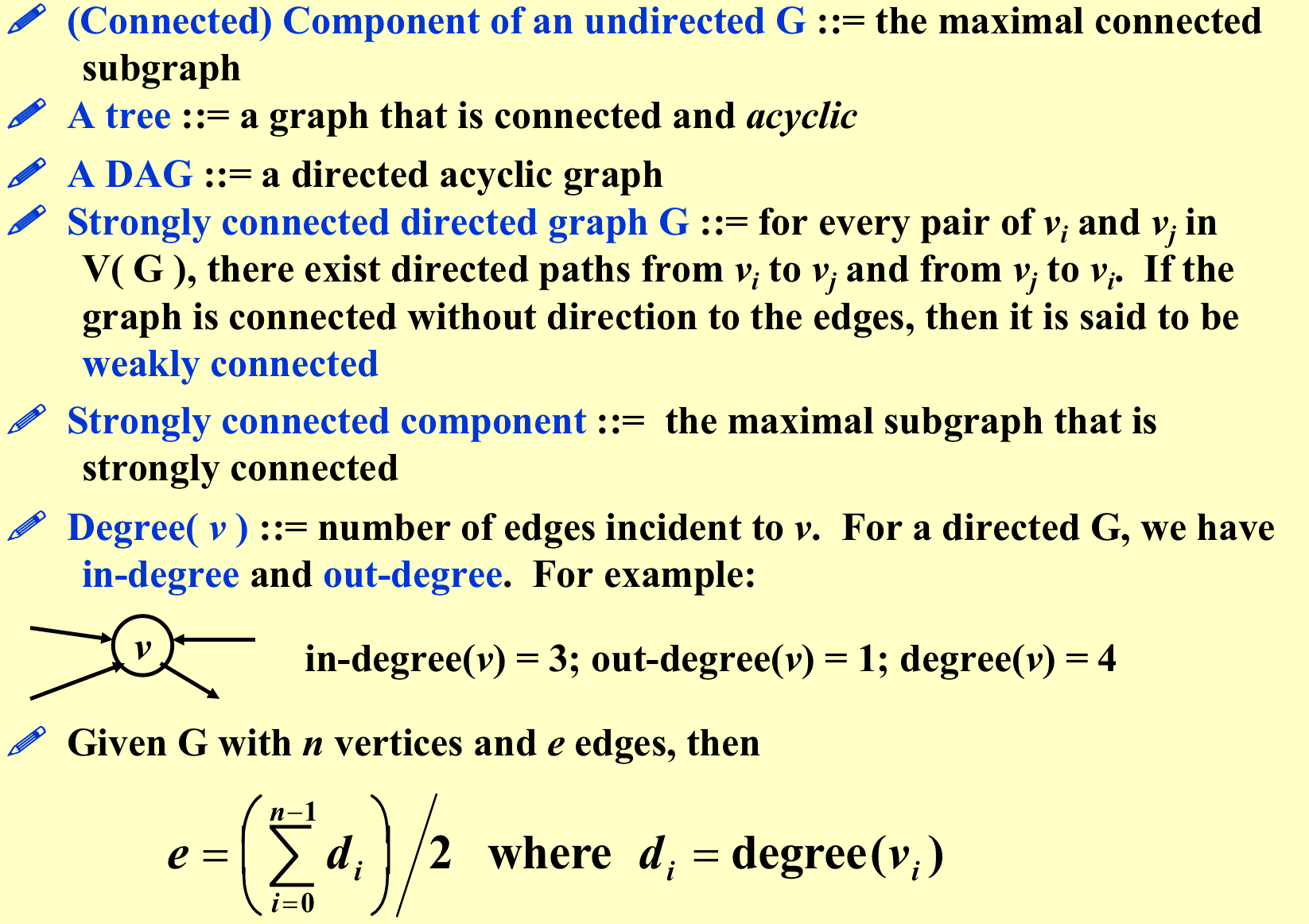
2. Representation of Graph¶
-
利用邻接矩阵的二维数组;
-
Adjacnecy Lists(邻接表):
指出去的结点连接起来的链表; 逆邻接表:指向自己的结点连接起来的链表;
本文总阅读量次